Match the label to its appropriate region of the brainstem – Embarking on a journey to decipher the intricacies of the brainstem, we present a comprehensive guide to matching labels to their corresponding regions. This exploration delves into the functional and structural aspects of the medulla oblongata, pons, midbrain, and cerebellum, unraveling their vital roles in regulating various physiological processes.
Through a blend of lucid explanations, illustrative tables, and insightful discussions, we illuminate the intricate connections between structure and function within the brainstem, providing a deeper understanding of its essential role in maintaining homeostasis and coordinating complex behaviors.
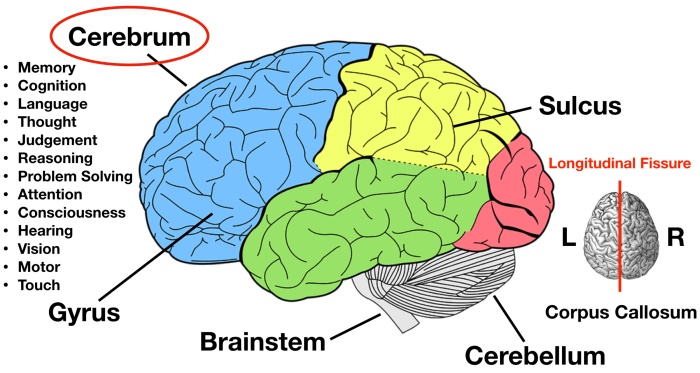
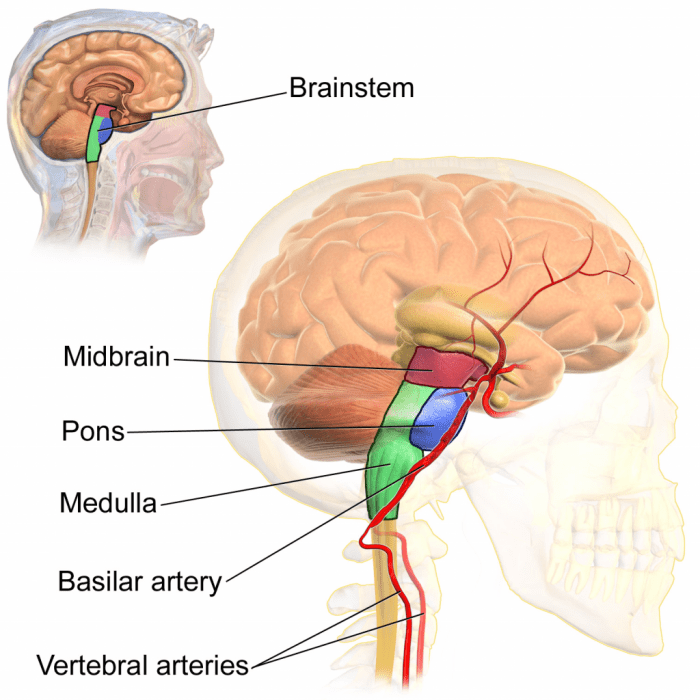
Match the Label to Its Appropriate Region of the Brainstem: Medulla Oblongata
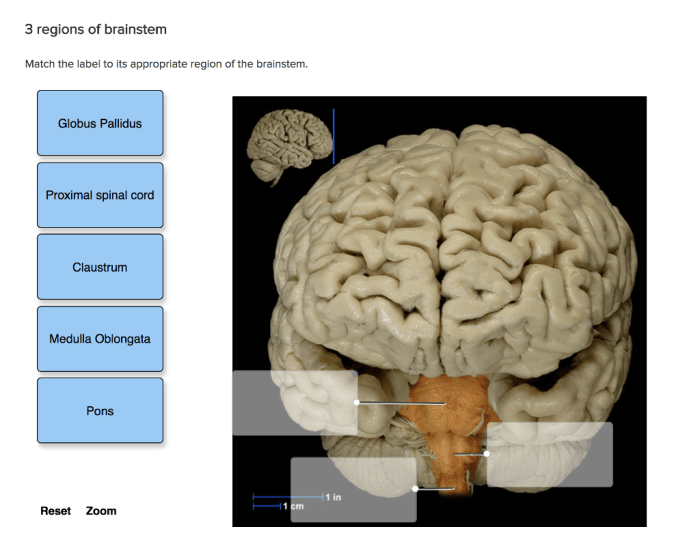
The medulla oblongata, also known as the myelencephalon, is the lowest and most caudal part of the brainstem. It is continuous with the spinal cord and connects to the pons and cerebellum. The medulla oblongata plays a crucial role in controlling vital life functions such as breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure.
Functions of the Medulla Oblongata, Match the label to its appropriate region of the brainstem
- Control of respiration: The medulla oblongata contains the respiratory center, which regulates the rate and depth of breathing.
- Control of heart rate and blood pressure: The medulla oblongata contains the cardiovascular center, which regulates the heart rate and blood pressure.
- Reflexes: The medulla oblongata contains several reflex centers, including the swallowing reflex, coughing reflex, and vomiting reflex.
- Relay of sensory and motor information: The medulla oblongata relays sensory information from the spinal cord to the higher brain centers and motor information from the higher brain centers to the spinal cord.
Location and Structure of the Medulla Oblongata
The medulla oblongata is located at the base of the brainstem, just above the spinal cord. It is a cone-shaped structure with a central canal that continues the central canal of the spinal cord.
The medulla oblongata is divided into two halves by a median sulcus. The dorsal surface of the medulla oblongata contains several nuclei, including the nucleus gracilis and nucleus cuneatus, which receive sensory information from the spinal cord. The ventral surface of the medulla oblongata contains the pyramids, which are motor tracts that carry motor information from the higher brain centers to the spinal cord.
Table of Labels and Corresponding Regions in the Medulla Oblongata
| Label | Region |
|---|---|
| Nucleus gracilis | Receives sensory information from the lower body |
| Nucleus cuneatus | Receives sensory information from the upper body |
| Pyramids | Carry motor information from the higher brain centers to the spinal cord |
| Respiratory center | Regulates the rate and depth of breathing |
| Cardiovascular center | Regulates the heart rate and blood pressure |
Questions Often Asked: Match The Label To Its Appropriate Region Of The Brainstem
What is the primary function of the medulla oblongata?
The medulla oblongata controls vital life-sustaining functions such as respiration, heart rate, and blood pressure.
Where is the pons located?
The pons is situated between the midbrain and the medulla oblongata, forming the ventral portion of the brainstem.
What is the role of the midbrain in motor control?
The midbrain houses nuclei involved in coordinating eye movements, head orientation, and muscle tone.